
Lesson Plan Geometric Shapes (Circle, Square, Triangle).
Trigonometry (Yoshiwara) 1: Triangles and Circles
Circle In The Triangle ClipArt Best
In terms of formulas, the circle is defined as- ( x ) 2 ( y ) 2 R 2 ,where [x,y]=[ , ] is the circle center and R its radius. If we center the circle on the origin such that = =0 and choose three points A, B, and C on the circle and then connect these points with straight lines, the following triangle will result.

Circles and triangles wallpaper Happywall
Examples, videos, games, activities, and worksheets to help ACT students review properties of triangles and circles. This video briefly explains the properties of a triangle. It also explains the classification of triangles based on angles and side length ratios of triangles. The triangle sum theorem is explained and used in a few applications.

geometry How can I work out the length of the sides of an Equilateral
Bisect the angle. Pick a point on the bisector. From that point construct perpendiculars through that point to each of the two sides of the angle. Show that the two triangles formed are congruent. Since the point is arbitrary, it means that any point on the bisector is equidistant from both sides of the triangle.
Circle Made Up Of Triangles ClipArt ETC
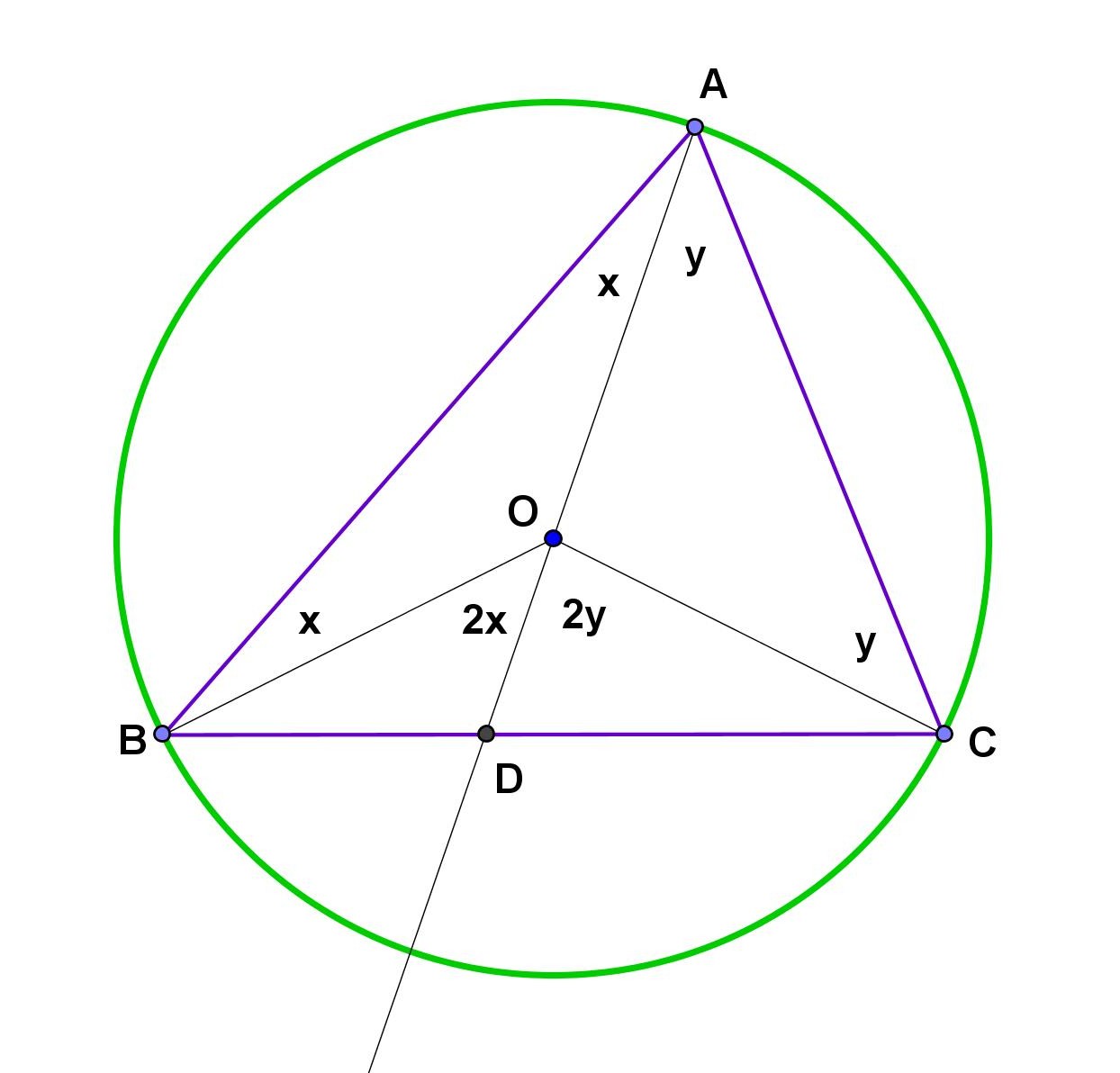
Some interesting things about angles and circles Inscribed Angle First off, a definition: Inscribed Angle: an angle made from points sitting on the circle's circumference. A and C are "end points" B is the "apex point" Play with it here: When you move point "B", what happens to the angle? Inscribed Angle Theorems Keeping the end points fixed.
Triangle Inscribed In A Circle ClipArt ETC
This common ratio has a geometric meaning: it is the diameter (i.e. twice the radius) of the unique circle in which \(\triangle\,ABC\) can be inscribed, called the circumscribed circle of the triangle. Before proving this, we need to review some elementary geometry. Figure 2.5.1 Types of angles in a circle

Circle And Triangle Symbol ClipArt Best
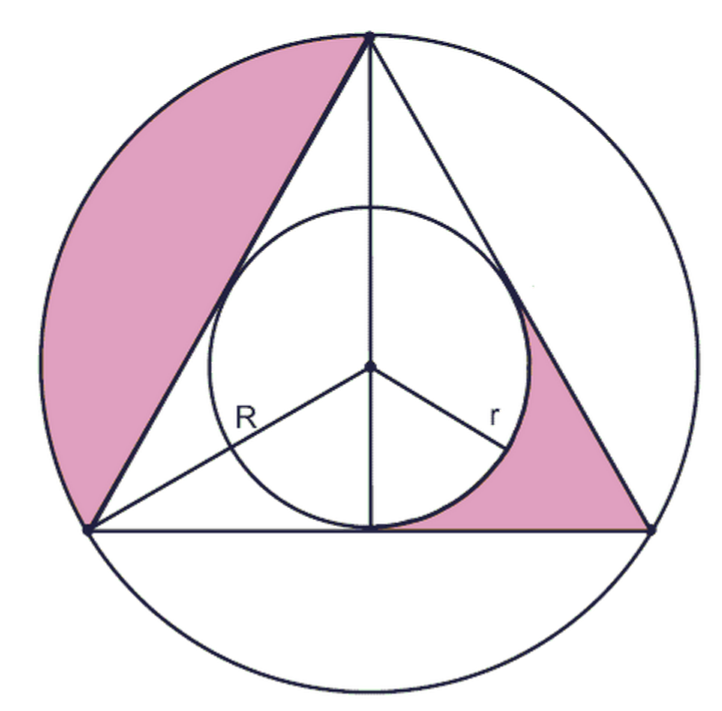
The area of a circumscribed triangle is given by the formula \frac {1} {2} \times r \times (\text {the triangle's perimeter}), 21 ×r ×(the triangle's perimeter), where r r is the inscribed circle's radius. Therefore the answer is \frac {1} {2} \times 3 \times 30 = 45. \ _\square 21 ×3× 30 = 45.

3 Ways to Determine a Triangle and Circle of Equal Area wikiHow
Geometry Interactive, free online geometry tool from GeoGebra: create triangles, circles, angles, transformations and much more!
Area of Circle with Triangles ClipArt ETC
Categories Have you noticed that the circle and triangle symbol no longer appears at the top of the Grapevine's Table of Contents? The decision to remove it has its roots in recent events: actions of the 1993 General Service Conference, and subsequent actions by the Board of Trustees and the directors of AA World Services.

Trigonometry Definition, Formulas, Ratios, & Identities Britannica
Khan Academy Kids 224K subscribers Subscribe Subscribed 113 48K views 1 year ago Shapes Shapes can be described by counting their sides and their corners. Learn about the attributes of these shapes.

Inscribed and Circumscribed Figures Level 3 Challenges Practice
The Research Triangle, or simply The Triangle, are both common nicknames for a metropolitan area in the Piedmont region of the U.S. state of North Carolina.Anchored by the cities of Raleigh and Durham and the town of Chapel Hill, the region is home to three major research universities: North Carolina State University, Duke University, and the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill.

Triangle And Circle Free Stock Photo Public Domain Pictures
Triangles and Circles Theorems on Circles and Triangles including a proof of the Pythagoras Theorem View other versions (2) Contents Statements Of Some Theorems On The Circle. Statements Of Some Theorems On Proportions And Similar Triangles. Pythagoras Theorem Two Theorems On Similar Rectilinear Figures. Page Comments
Circle In The Triangle ClipArt Best
Unit 14 Circles Unit 15 Analytic geometry Unit 16 Geometric constructions Unit 17 Miscellaneous Math Geometry (all content) Unit 14: Circles About this unit Explore, prove, and apply important properties of circles that have to do with things like arc length, radians, inscribed angles, and tangents. Circle basics Learn Circles glossary
Math Principles Proving Inscribed Triangle, Circle
Let's break the area into two parts: Part A is a square: Area of A = a 2 = 20m × 20m = 400m 2. Part B is a triangle. Viewed sideways it has a base of 20m and a height of 14m. Area of B = ½b × h = ½ × 20m × 14m = 140m 2. So the total area is: Area = Area of A + Area of B = 400m 2 + 140m 2 = 540m 2. Sam earns $0.10 per square meter.

Math Principles Circle Inscribed Triangle Problems
Noble Mushtak. [cos (θ)]^2+ [sin (θ)]^2=1 where θ has the same definition of 0 above. This is similar to the equation x^2+y^2=1, which is the graph of a circle with a radius of 1 centered around the origin. This is how the unit circle is graphed, which you seem to understand well.
Circle & Triangle Openclipart
A circle O is circumscribed around a triangle ABC, and its radius is r. The angles of the triangle are CAB = a, ABC = b, BCA = c. When a = 75°, b = 60°, c = 45° and r = 1, the length of sides AB, BC, and CA are calculated as ____, ____, ____ without using trigonometric functions. Here is a picture showing all the information we have: