
Download Binomial Probability Distribution Table N 20 Gantt Chart
The outcomes of a binomial experiment fit a binomial probability distribution. The random variable X = the number of successes obtained in the n independent trials. The mean, μ, and variance, σ2, for the binomial probability distribution are μ = np and σ2 = npq. The standard deviation, σ, is then σ = npq−−−√ n p q.
Binomial Table PDF
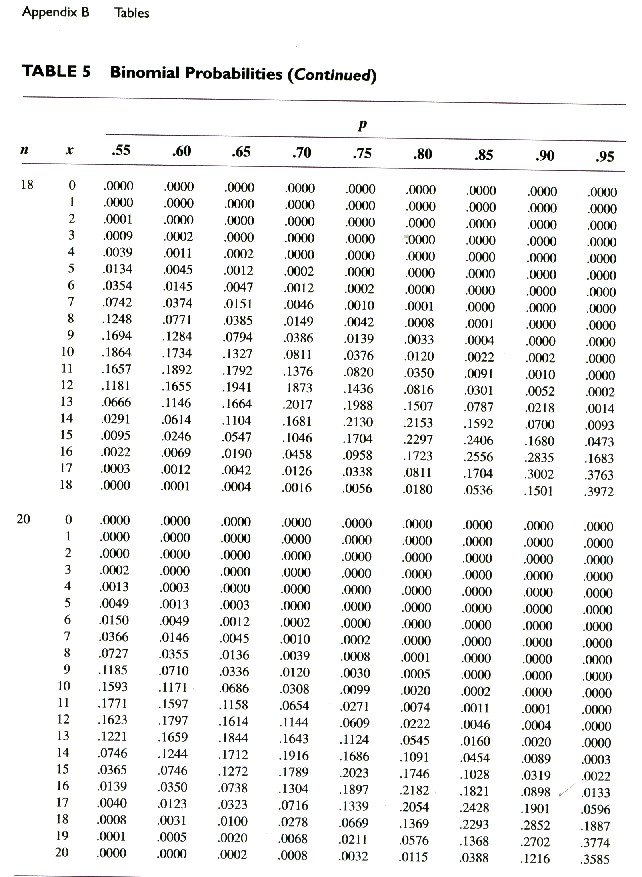
The binomial distribution, which gives the probabilities for the values of this type of variable, is completely determined by two parameters: n and p. Here n is the number of trials and p is the probability of success on that trial. The tables below are for n = 10 and 11. The probabilities in each are rounded to three decimal places.

Peter's Statistics Crash Course
Table 4 Binomial Probability Distribution C p r qn − r n, r This table shows the probability of r successes in n independent trials, each with probability of success p. The table entries represent the area under the standard normal curve from 0 to the specified value of z.

Tabel Binomial PDF
The binomial table is used to perform nonparametric tests on statistics that are distributed according to binomial distribution, especially the sign test and the binomial test. The National Bureau of Standards (1950) published individual and cumulative binomial distribution probabilities for \( { n \leq 49 } \), while cumulative binomial distribution probabilities for \( { n\!\!\leq\!\!1000.
PPT Chapter 7 PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID6846699
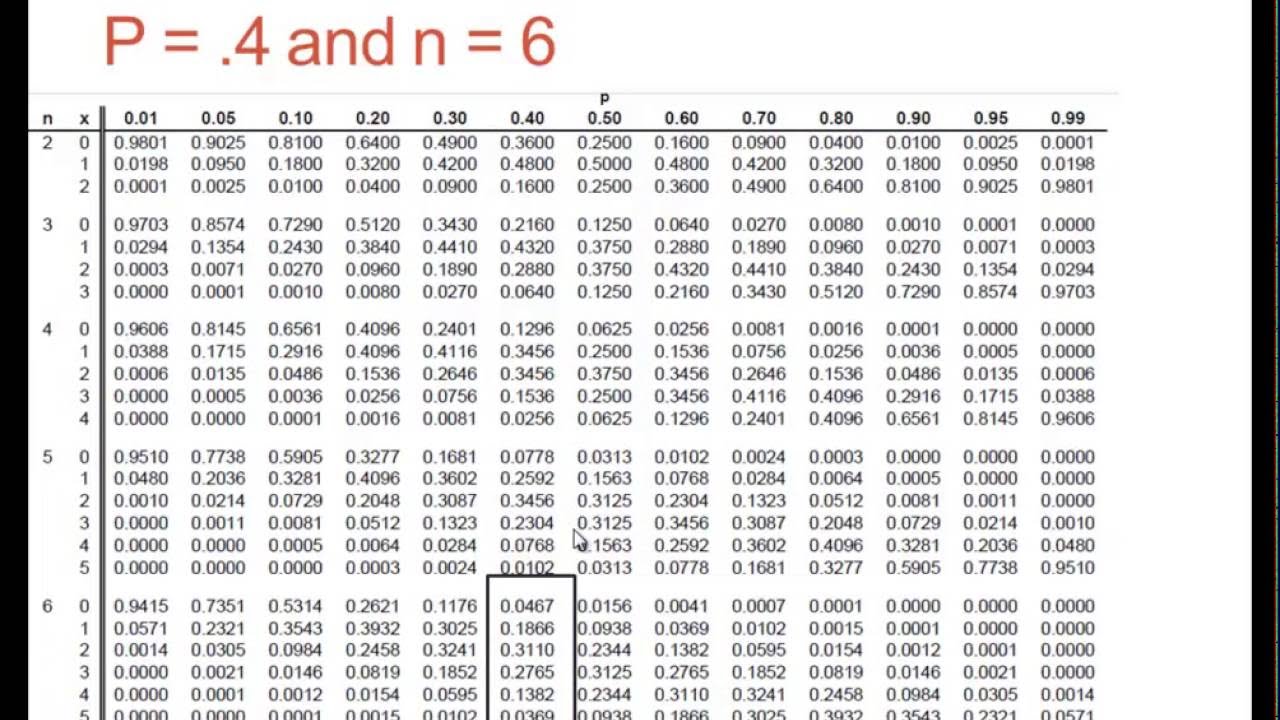
The binomial distribution describes the probability of obtaining k successes in n binomial experiments. If a random variable X follows a binomial distribution, then the probability that X = k successes can be found by the following formula: P (X=k) = nCk * pk * (1-p)n-k. where: n: number of trials. k: number of successes.

Tabla Binomial Completa Ing
Other Tables . For other binomial distribution tables: n = 7 to 9, n = 10 to 11. For situations in which np and n(1 - p) are greater than or equal to 10, we can use the normal approximation to the binomial distribution. In this case, the approximation is very good and does not require the calculation of binomial coefficients.

pgfmath Binomial distribution in table TeX LaTeX Stack Exchange
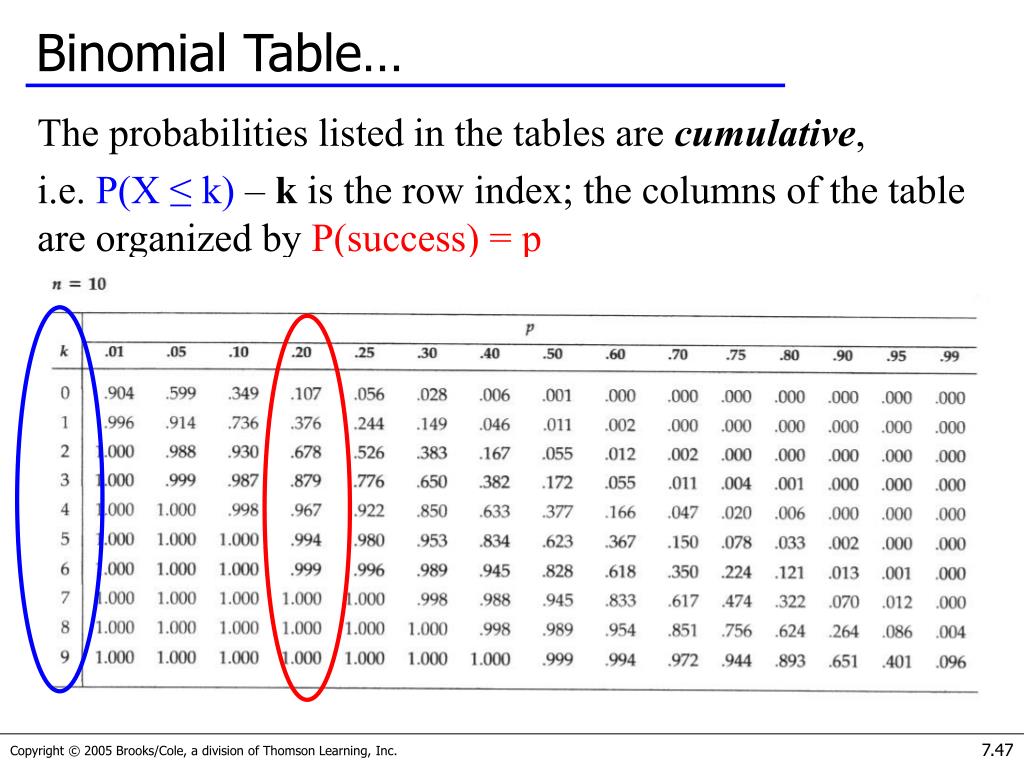
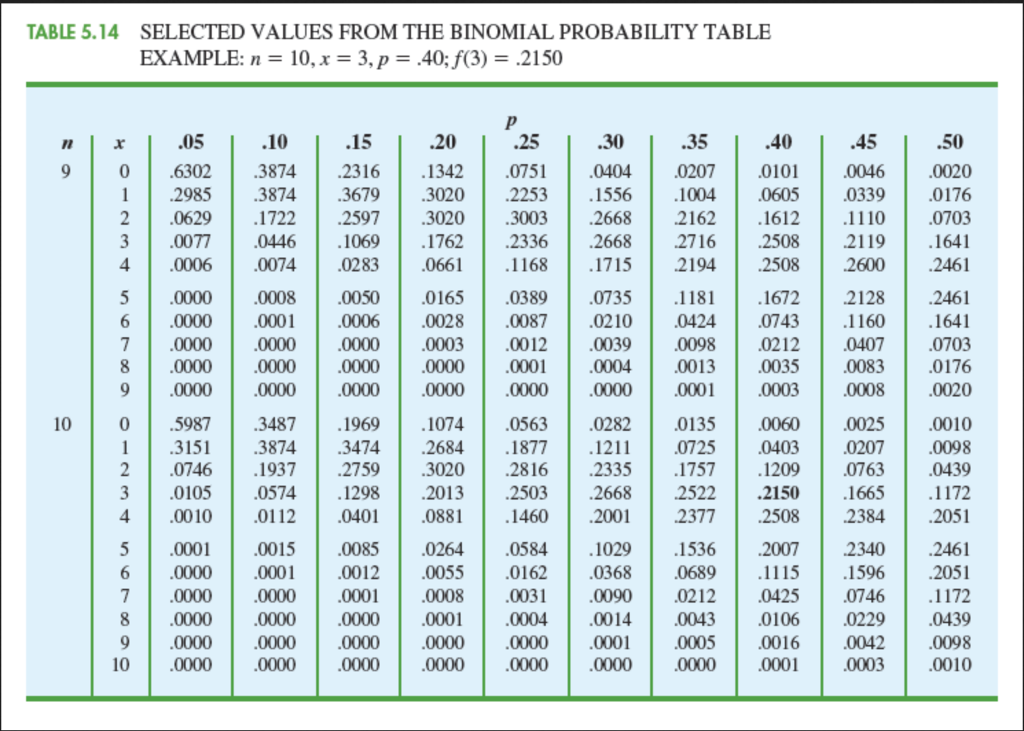
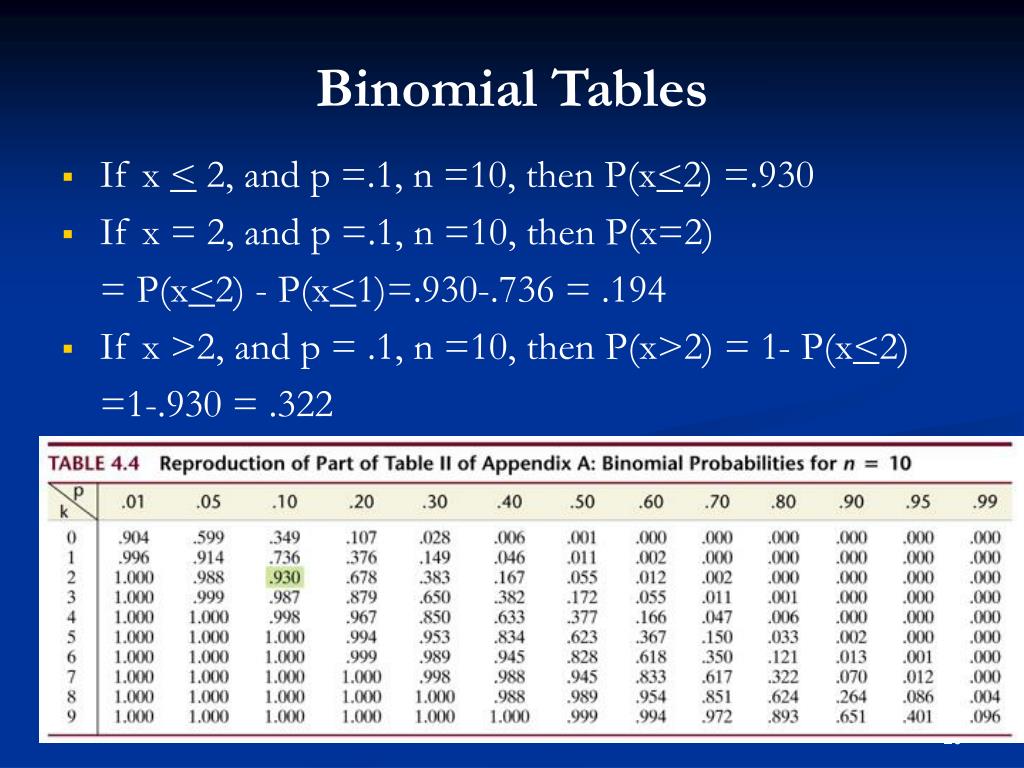
To find each of these probabilities, use the binomial table, which has a series of mini-tables inside of it, one for each selected value of n. To find P ( X = 0), where n = 11 and p = 0.4, locate the mini-table for n = 11, find the row for x = 0, and follow across to where it intersects with the column for p = 0.4. This value is 0.004.
Binomial Distribution Using the Probability Tables YouTube
The binomial distribution table is a table that shows probabilities associated with the binomial distribution.To use the binomial distribution table, you only need three values: n: the number of trials r: the number of "successes" during n trials p: the probability of success on a given trial Using these three numbers, you can use the binomial distribution table to find the probability of.
Solved Note This question is not this is the
To understand how cumulative probability tables can simplify binomial probability calculations. To learn how to read a standard cumulative binomial probability table. To learn how to determine binomial probabilities using a standard cumulative binomial probability table when \(p\) is greater than 0.5.

Binomial Probability Distribution Table Pdf
The binomial table of probabilities shows the probability of success in a trial. This table uses n, the number of trials, r or x, the number of successes, and p, probability. For example, suppose.

How to Read the Binomial Distribution Table Statology
How to Read a Binomial Distribution Table. Binomial Distribution Table. This binomial distribution table has the most common cumulative probabilities listed for n. Homework or test problems with binomial distributions should give you a number of trials, called n. Click the link below that corresponds to the n from your problem to take you to.
PPT Chapter 4 PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID726350
In probability theory and statistics, the binomial distribution with parameters n and p is the discrete probability distribution of the number of successes in a sequence of n independent experiments,. In creating reference tables for binomial distribution probability, usually the table is filled in up to n/2 values.
binomial
The calculator displays a binomial probability of 15.51%, matching our results above for this specific number of sixes. Next, change exactly r successes to r or more successes. The calculator displays 22.487, matching the results for our example with the binomial inverse cumulative distribution. Now, try one yourself.

Download Binomial Probability Distribution Table N 20 Gantt Chart
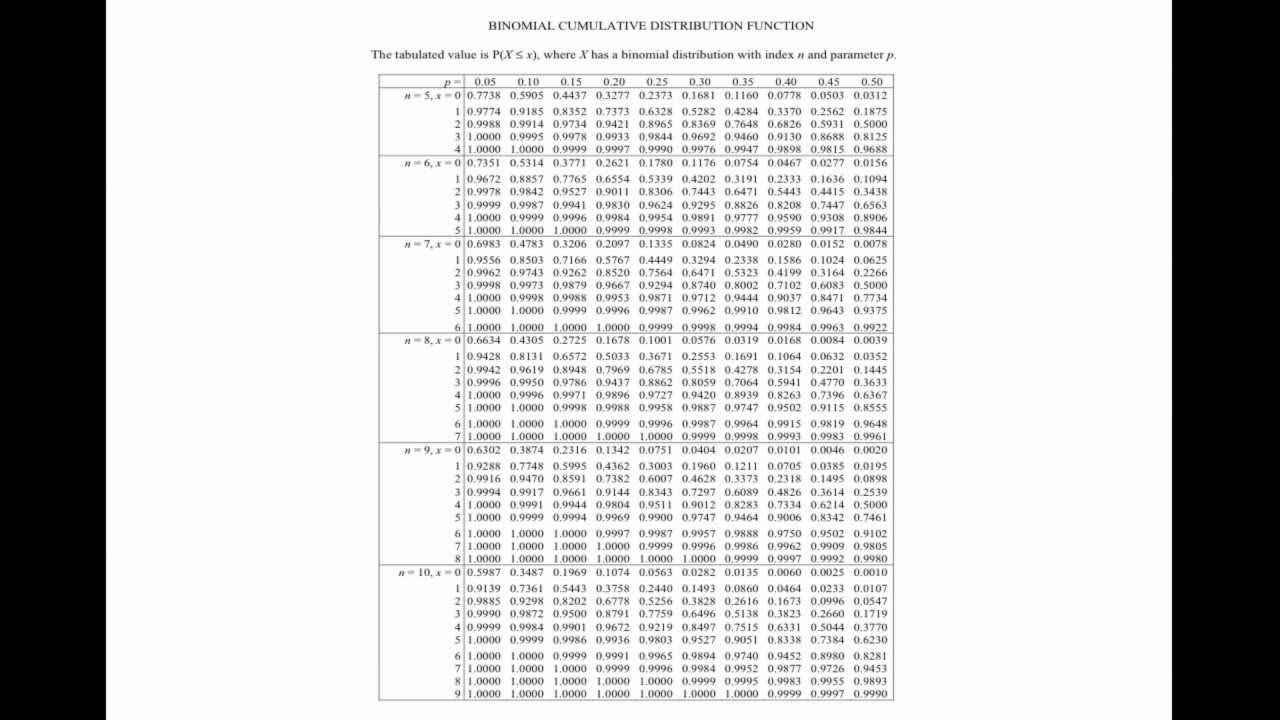
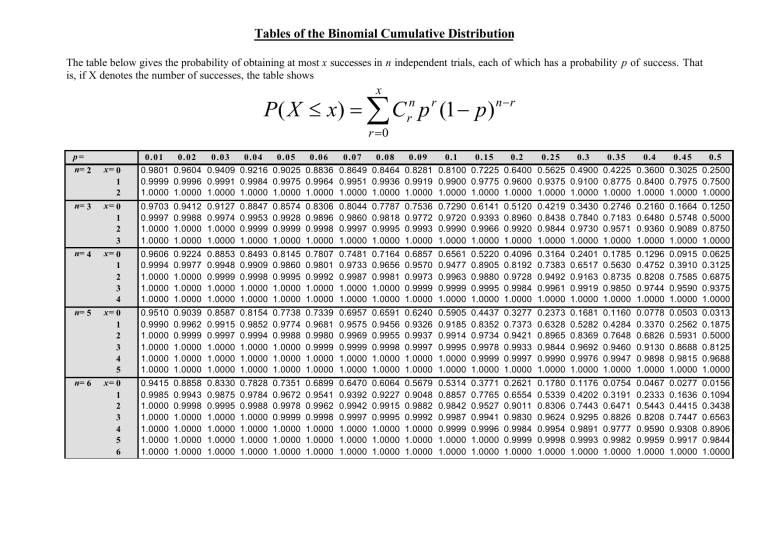
Tabl e: Cumulative Binomial probabilities 1 [ ] ∑ ( ) − − ≤ = c x p nx x n P X c 0 1 p c 0.05 0.10 0.20 0.30 0.40 0.50 0.60 0.70 0.80 0.90 0.95
Binomial probability
The binomial distribution formula is: b(x; n, P) = n C x * P x * (1 - P) n - x Where: b = binomial probability x = total number of "successes" (pass or fail, heads or tails etc.) P = probability of a success on an individual trial n = number of trials Note: The binomial distribution formula can also be written in a slightly different way, because n C x = n! / x!(n - x)!
Download Binomial Probability Distribution Table N 20 Gantt Chart
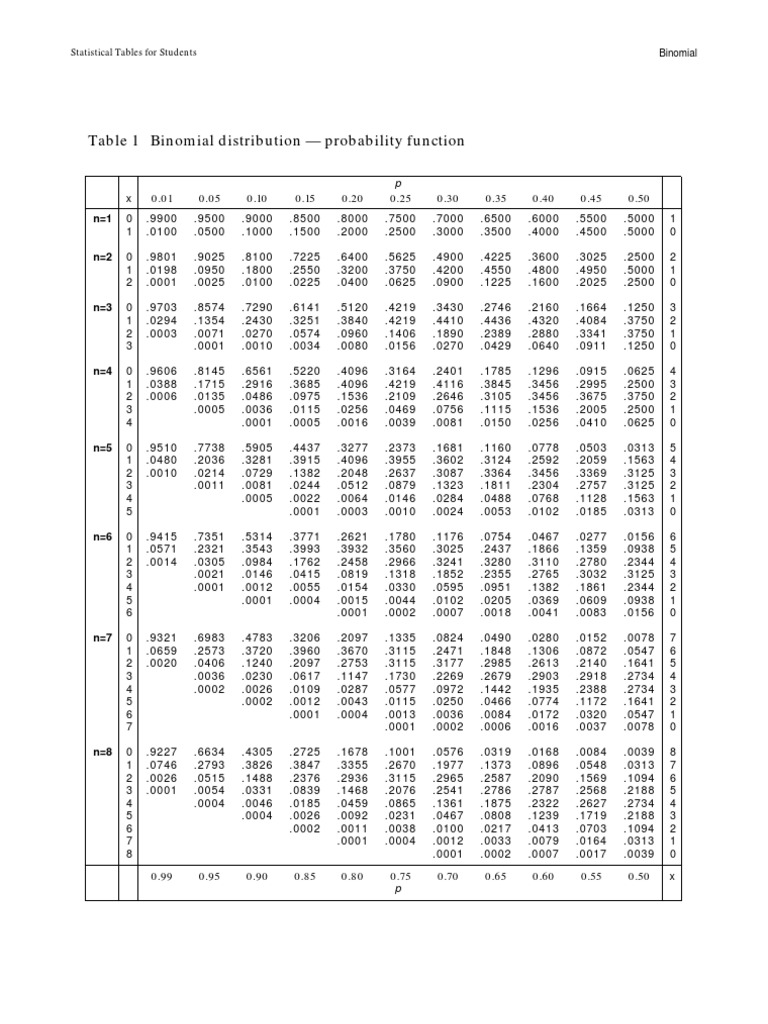
Binomial Probability Distribution Table This table shows the probability of x successes in n independent trials, each with probability of success p. n x 0.01 0.05 0.1 0.15 0.2 0.25 0.3 0.35 0.4 0.45 0.5 0.55 0.6 0.65 0.7 0.75 0.8 0.85 0.9 0.95